Introduction to Multi-Agent Architectures in AI
2025 marks a pivotal year for artificial intelligence, with multi-agent architectures emerging as the dominant framework for complex, real-world problem-solving. As organizations push beyond basic AI implementations, the limitations of single-agent systems have become increasingly evident. This article serves as your primer to multi-agent systems—setting the stage for deeper exploration and equipping you with a solid foundation for future innovations.
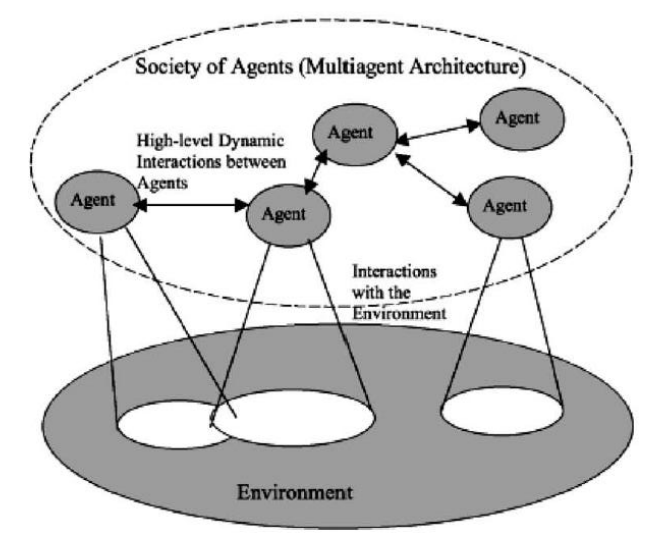
What Are Multi-Agent Systems?
Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) are collaborative networks of autonomous AI agents that work together to accomplish tasks that would be difficult or impossible for a single agent to achieve efficiently. In a multi-agent architecture, each agent is specialized, often leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) as their cognitive engine, and together they negotiate, coordinate, and sometimes compete to reach both individual and collective objectives.
Unlike traditional, monolithic AI systems with a central authority dictating every move, multi-agent architectures distribute decision-making across the network. This decentralized approach mirrors real-world teamwork and is particularly effective in dynamic, unpredictable environments.
Comparison with Single-Agent Systems
| Feature | Single-Agent Systems | Multi-Agent Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Isolated task execution | Collaborative problem-solving |
| Resilience | Single point of failure | Fault-tolerant via redundancy |
| Scalability | Limited vertical scaling | Horizontal scaling via new agents |
| Problem Handling | Structured, predictable tasks | Dynamic, complex environments |
| Communication | None (self-contained) | Negotiation/coordination protocols |
Single agents excel in controlled, predictable scenarios (e.g., a chess-playing AI), while multi-agent systems thrive in chaotic real-world contexts like disaster response or supply chain optimization.
Why 2025 Is Significant
2025 stands out for multi-agent architectures due to three converging trends:
- Complexity Demands: Enterprises now face problems too intricate for single agents, such as real-time supply chain optimization or adaptive customer service.
- Specialization Needs: Domain-specific expertise (e.g., healthcare diagnostics, fraud detection) requires dedicated agents.
- Framework Maturity: Platforms like LangChain and AutoGen now streamline MAS deployment, reducing development barriers and making multi-agent solutions more accessible.
Core Components of Multi-Agent Systems
Every effective multi-agent system relies on three essential components:
Intelligent Agents
These autonomous entities are the foundation of any multi-agent system. Each agent focuses on specific responsibilities and operates independently while collaborating with others. Modern agents often use LLMs for reasoning, enabling human-like contextual understanding and complex decision-making.
Orchestration Mechanisms
Much like a symphony conductor, orchestration mechanisms define how agents interact, allocate tasks, and manage information flow. Well-designed orchestration ensures the entire system operates smoothly and efficiently, enabling dynamic task assignment, conflict resolution, and workflow control.
Communication Protocols
Standardized ways for agents to exchange information and intentions form the backbone of any multi-agent system. Communication can include structured message formats (like JSON or XML), reliable transport layers (such as HTTP or MQTT), and established interaction patterns (like publish-subscribe or request-reply). Interoperability standards, such as FIPA ACL, ensure agents from different platforms can work together seamlessly.
This introduction sets the stage for exploring the practical patterns and real-world applications of multi-agent architectures in the next article. Stay tuned for a deep dive into the patterns that power industries from healthcare to finance.
Sources:
- Thesis: Quality Measurement Challenges for AI - Researchgate [researchgate.net/publication/309772147_Quality_Measurement_Challenges_for_Artificial_Intelligence_Software][1]
- Multi-AI Agents in 2025: Key Insights, Examples, and Challenges
[ioni.ai/post/multi-ai-agents-in-2025-key-insights-examples-and-challenges][2] - AI Agent Architectures: Modular, Multi-Agent, and Evolving – ProjectPro
[projectpro.io/article/ai-agent-architectures/1135][3] - Everything you need to know about multi AI agents in 2025 – Springs
[springsapps.com/knowledge/everything-you-need-to-know-about-multi-ai-agents-in-2024-explanation-examples-and-challenges][4] - The Best Open Source Frameworks For Building AI Agents in 2025 – Firecrawl
[firecrawl.dev/blog/best-open-source-agent-frameworks-2025][5]