IPv6: The Evolutionary Step in Modern Networking
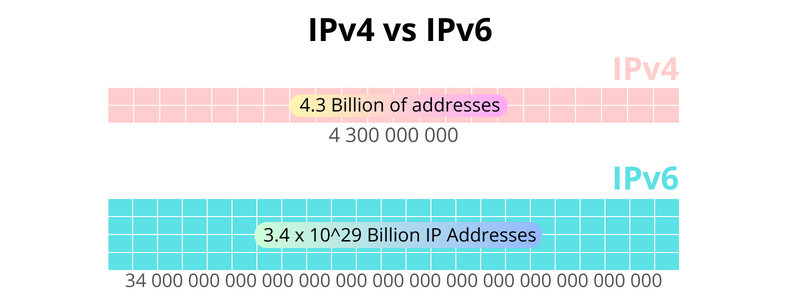
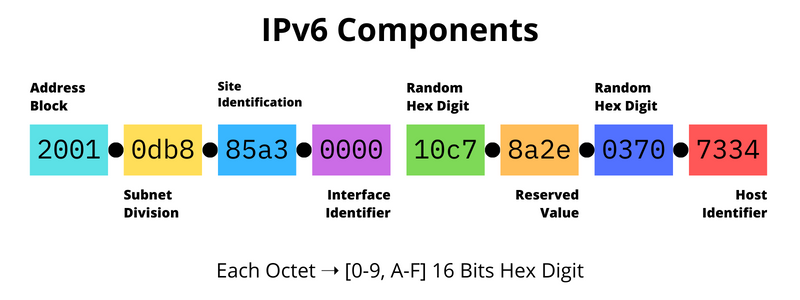
The introduction of IPv6 was not just an expansion of address space but a complete overhaul to meet the demands of modern networking. With an almost inexhaustible number of IP addresses, IPv6 lays the groundwork for an increasingly interconnected world. Its 128-bit addresses ensure that we won’t run out of IP addresses anytime soon, considering the explosive growth of devices, often referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT).
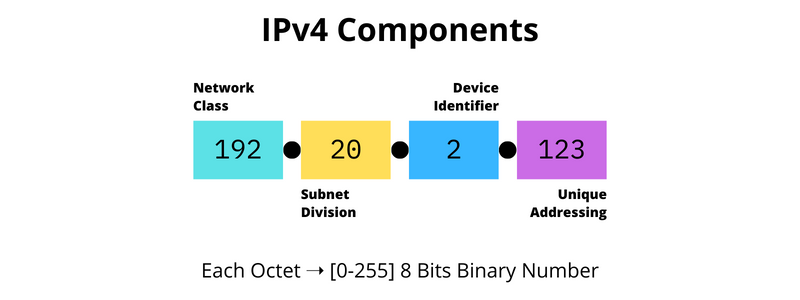
IPv4, with its 32-bit address space, was created at a time when the internet was in its infancy. No one could have predicted the massive surge in the number of connected devices, leading to a quick depletion of its address pool. The scarcity led to numerous workarounds, like Network Address Translation (NAT), which although functional, introduced complexities and impacted end-to-end connectivity.
IPv6 not only remedies the address shortage but introduces several improvements:
Abundant Address Space: 340 undecillion addresses. This makes subnetting simpler and addresses the needs of future generations.
Improved Network Performance: With simplified header structures, routers can process data packets more swiftly.
Auto Configuration Capabilities: Devices can self-configure their IP addresses, reducing the need for manual IP address configuration or DHCP.
NAT-Free End-to-End Communication: With such a vast address space, devices can have unique global addresses, enabling true end-to-end communication without relying on NAT.
Better Quality of Service (QoS) for Real-Time Apps: IPv6 allows for better handling of data packets, which is critical for real-time applications like VoIP and online gaming.
Enhanced Security: Built-in IPsec features in IPv6 ensure encrypted and authenticated communication, making the network more secure by default.
The transition, however, isn’t without challenges. Many legacy systems still run on IPv4, and the world needs both infrastructural and knowledge investment to migrate smoothly. Internet service providers, enterprises, and end-users all play a role in this transition. IPv6 adoption requires changes in hardware, software, security practices, and more.
However, the advantages are evident. As cloud computing, IoT, and the general trend towards everything-as-a-service continue to grow, IPv6’s importance becomes paramount. Its abundant address space and enhanced features promise a faster, more secure, and efficient internet for everyone.
In conclusion, while the journey from IPv4 to IPv6 might be long and filled with challenges, the destination is clear: a better-connected and more secure future. IPv6 isn’t just the future; it’s the path to sustain the ever-growing digital universe.